STUDY/Coding Test
[하계 코딩테스트 특강] 2022.07.07 배열 시뮬레이션
sseni
2022. 7. 7. 16:56
728x90
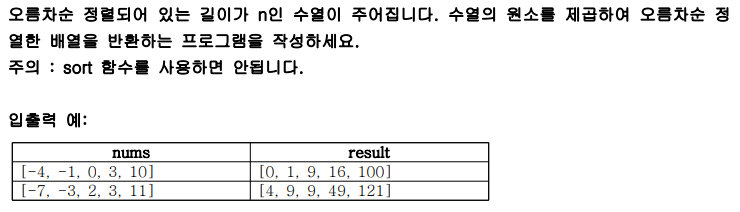
1) 제곱수 정렬
- java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public int[] solution(int[] arr){
int n = arr.length;
int[] ans = new int[n];
int left = 0;
int right = n-1;
for(int i=n-1; i >= 0; i--){
if(Math.abs(arr[left]) < Math.abs(arr[right])){
ans[i] = arr[right] * arr[right];
right--;
} else {
ans[i] = arr[left] * arr[left];
left++;
}
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Main T = new Main();
int[] tmp = new int[]{-4, -1, 0, 3, 10};
// System.out.println(T.solution(tmp));
for(int x : T.solution(tmp))
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
}- python
def solution(nums):
n=len(nums)
answer=[0]*n
left=0
right=n-1
for i in range(n-1, -1, -1):
if abs(nums[left])<abs(nums[right]):
tmp=nums[right]
right-=1
else:
tmp=nums[left]
left+=1
answer[i]=tmp*tmp
return answer
print(solution([-4, -1, 0, 3, 10]))
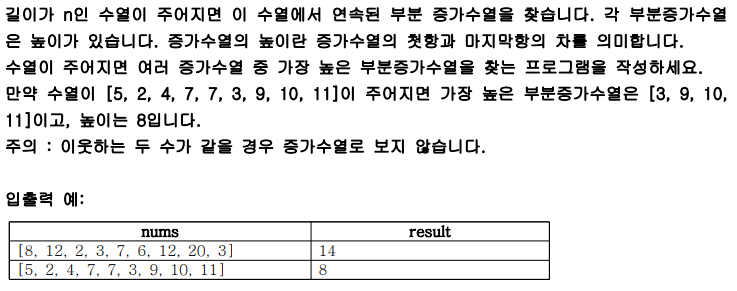
print(solution([-7, -3, 2, 3, 11]))2) 가장 높은 증가수열
- java
package ch02;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class 가장높은증가수열 {
public int solution(int[] arr){
int height = 0;
int ans = 0;
for(int i=1; i < arr.length; i++){
if(arr[i-1] < arr[i])
height += (arr[i] - arr[i-1]);
else {
ans = height > ans ? height : ans;
height = 0;
}
}
ans = height > ans ? height : ans;
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
가장높은증가수열 T = new 가장높은증가수열();
int[] tmp = new int[]{8, 12, 2, 3, 7, 6, 12, 20, 3};
int[] tmp1 = new int[]{5, 2, 4, 7, 7, 3, 9, 10, 11};
System.out.println(T.solution(tmp1));
}
}- python
def solution(nums):
answer=0
height=0
n=len(nums)
for i in range(1, n):
if nums[i-1]<nums[i]:
height+=(nums[i]-nums[i-1])
else:
answer=max(answer, height)
height=0
answer=max(answer, height)
return answer
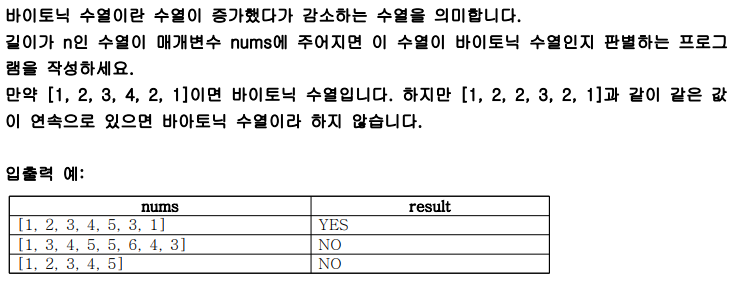
print(solution([5, 2, 4, 7, 6, 3, 9, 10, 11]))3) 바이토닉 수열
- java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public String solution(int[] arr){
String ans = "YES";
int n = arr.length;
int i = 0;
while(i+1 < n && arr[i] < arr[i+1]) i++;
if(i == 0 || i == n-1) return "NO"; // 처음부터 감소하거나 끝까지 감소할 때
while(i+1 < n && arr[i] > arr[i+1]) i++;
if(i != n-1) return "NO";
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Main T = new Main();
int[] tmp = new int[]{1,2,3,5,5,3,1};
System.out.println(T.solution(tmp));
}
}- python
def solution(nums):
answer="YES"
n=len(nums)
i=0
while i+1<n and nums[i]<nums[i+1]:
i+=1
if i==0 or i==n-1:
return "NO"
while i+1<n and nums[i]>nums[i+1]:
i+=1
if i!=n-1:
return "NO"
return answer
print(solution([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 3, 1]))4) 최대길이 바이토닉

- java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public int solution(int[] nums){
int answer=0;
int n=nums.length;
ArrayList<Integer> peaks = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=1; i<n-1; i++){
if(nums[i-1]<nums[i] && nums[i]>nums[i+1]){
peaks.add(i);
}
}
for(int x : peaks){
int lt = x;
int rt = x;
int cnt = 1;
while(lt-1>=0 && nums[lt-1]<nums[lt]){
lt--;
cnt++;
}
while(rt+1<n && nums[rt]>nums[rt+1]){
rt++;
cnt++;
}
answer=Math.max(answer, cnt);
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Main T = new Main();
int[] tmp = new int[]{1, 3, 2, 5, 7, 4, 2, 5, 1};
System.out.println(T.solution(tmp));
}
}- python
def solution(nums):
answer=0
peaks=[]
n=len(nums)
for i in range(1, n-1):
if nums[i-1]<nums[i] and nums[i]>nums[i+1]:
peaks.append(i)
for pos in peaks:
lt=pos
rt=pos
cnt=1
while lt>=1 and nums[lt-1]<nums[lt]:
cnt+=1
lt-=1
while rt<n-1 and nums[rt]>nums[rt+1]:
cnt+=1
rt+=1
answer=max(answer, cnt)
return answer
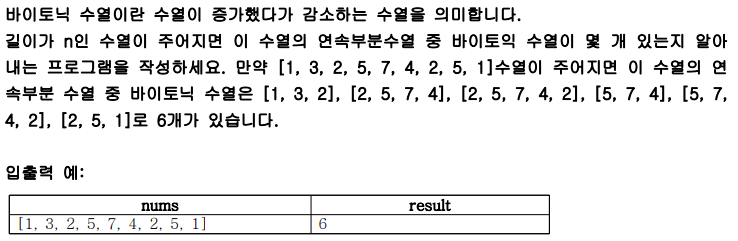
print(solution([1, 3, 2, 5, 7, 4, 2, 5, 1]))5) 수열의 경우수
- java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public int solution(int[] nums){
int answer=0;
int n=nums.length;
ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=1; i<n-1; i++){
if(nums[i-1]<nums[i] && nums[i]>nums[i+1]){
arr.add(i);
}
}
for(int x : arr){
int lt = x;
int rt = x;
int l = 0;
int r = 0;
while(lt-1>=0 && nums[lt-1]<nums[lt]){
lt--;
l++;
}
while(rt+1<n && nums[rt]>nums[rt+1]){
rt++;
r++;
}
answer += (l * r);
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Main T = new Main();
int[] tmp = new int[]{1, 3, 2, 5, 7, 4, 2, 5, 1};
System.out.println(T.solution(tmp));
}
}- python
def solution(nums):
answer=0
peaks=[]
n=len(nums)
for i in range(1, n-1):
if nums[i-1]<nums[i] and nums[i]>nums[i+1]:
peaks.append(i)
for pos in peaks:
lt=pos
rt=pos
lcnt=0
rcnt=0
while lt>=1 and nums[lt-1]<nums[lt]:
lcnt+=1
lt-=1
while rt<n-1 and nums[rt]>nums[rt+1]:
rcnt+=1
rt+=1
answer+=(lcnt*rcnt)
return answer
print(solution([1, 3, 2, 5, 7, 4, 2, 5, 1]))#6
print(solution([1, 2, 1, 2, 2, 7, 6, 5, 4, 5, 6, 7, 6, 3, 2, 1]))#16
print(solution([1, 2, 1, 2, 2, 5, 4, 3, 2, 3, 1]))#56) 거리두기
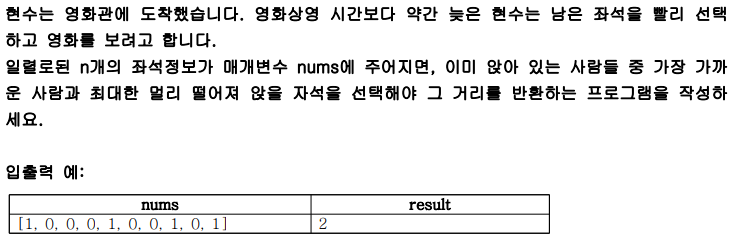
- java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public int solution(int[] nums){
int answer = 0;
int n = nums.length;
int[] dist = new int[n];
int d = 100000;
for(int i=0; i < n; i++){
if(nums[i] == 1) {
d = 0;
dist[i] = d;
} else {
d++;
dist[i] = d;
}
}
d = 100000;
for(int i=n-1; i >= 0; i--){
if(nums[i] == 1) d = 0;
else {
d++;
dist[i] = Math.min(dist[i], d);
}
}
for(int x : dist) answer = Math.max(x, answer);
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Main T = new Main();
int[] tmp = new int[]{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1};
System.out.println(T.solution(tmp));
}
}- python
def solution(nums):
answer=0
n=len(nums)
dist=[0]*n
d=1000
for i in range(n):
if nums[i]==1:
d=0
dist[i]=d
else:
d+=1
dist[i]=d
d=1000
for i in range(n-1, -1, -1):
if nums[i]==1:
d=0
else:
d+=1
dist[i]=min(dist[i], d)
answer=max(dist)
return answer
print(solution([1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1]))7) 키보드

- java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public int solution(String s, int n){
int[] used = new int[27]; // 0-26: 소문자, 27: shift 키
for(int c : s.toCharArray()){ // 소문자: 97-122, 대문자: 65-90
if(c >= 97 && c <= 122) used[c-97] = 1; // 소문자일 때
else if(c >= 65 && c <= 90) { // 대문자일 때
used[26] = 1;
used[c-65] = 1;
}
}
int cnt = 0;
for(int i=0; i < 27; i++){
if(used[i] == 1) cnt++;
}
if(cnt <= n) return s.length();
else return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Main T = new Main();
System.out.println(T.solution("Big Life is Good", 10));
}
}- python
def solution(s, n):
used = [0] * 27
for ele in s:
if ele.islower():
used[ord(ele)-97] = 1
elif ele.isupper():
used[26] = 1
used[ord(ele)-65] = 1
cnt = 0
for i in range(27):
if used[i] == 1:
cnt += 1
if cnt <= n:
return len(s)
else:
return -1
print(solution("time to time", 5))
print(solution("time to study", 7))
print(solution("Big Life is Good", 10))
print(solution("Life is Good", 7))8) 봉우리


- java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
int[] dx={-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] dy={0, 1, 0, -1};
public int solution(int[][] board){
int answer = 0;
int n = board.length;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
for(int j=0; j<n; j++){
boolean flag = true;
for(int k=0; k<4; k++){
int nx = i + dx[k];
int ny = j + dy[k];
if(nx>=0 && nx<n && ny>=0 && ny<n && board[nx][ny]>=board[i][j]){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if(flag) answer++;
}
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Main T = new Main();
int[][] arr={{5, 3, 7, 2, 3},
{3, 7, 1, 6, 1},
{7, 2, 5, 3, 4},
{4, 3, 6, 4, 1},
{8, 7, 3, 5, 2}};
System.out.println(T.solution(arr));
}
}- python
def solution(board):
n=len(board)
cnt=0
dx=[-1, 0, 1, 0]
dy=[0, 1, 0, -1]
board.insert(0, [0]*n)
board.append([0]*n)
for x in board:
x.insert(0, 0)
x.append(0)
cnt=0
for i in range(1, n+1):
for j in range(1, n+1):
if any(board[i][j]<=board[i+dx[k]][j+dy[k]] for k in range(4)):
continue
cnt+=1
return cnt
print(solution([[5, 3, 7, 2, 3],
[3, 7, 1, 6, 1],
[7, 2, 5, 3, 4],
[4, 3, 6, 4, 1],
[8, 7, 3, 5, 2]]))
9) 스카이라인


- java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public int solution(int[][] board){
int ans = 0;
int n = board.length;
int[] row = new int[n];
int[] col = new int[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
for(int j=0; j<n; j++){
if(board[i][j] > row[i]) row[i] = board[i][j];
if(board[j][i] > col[i]) col[i] = board[j][i];
}
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
for(int j=0; j<n; j++){
ans += Math.min(row[i], col[j]) - board[i][j];
}
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Main T = new Main();
int[][] arr={{2, 5, 7, 3},
{6, 8, 9, 7},
{3, 2, 4, 5},
{7, 2, 5, 8}};
System.out.println(T.solution(arr));
}
}- python
def solution(board):
answer=0
n=len(board)
row=[0]*n
col=[0]*n
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if board[i][j]>row[i]:
row[i]=board[i][j]
if board[j][i]>col[i]:
col[i]=board[j][i]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
answer+=(min(row[i], col[j])-board[i][j]);
return answer
print(solution([[2, 5, 7, 3], [6, 8, 9, 7], [3, 2, 4, 5], [7, 2, 5, 8]]))10) 회장선거

- java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public ArrayList<Integer> solution(int n, int[][] vote, int k){
ArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int[][] report = new int[n][n]; // 행 : 추천을 한 학생, 열 : 추천 받은 학생
int[] candidate = new int[n];
for(int[] x : vote) report[x[0]][x[1]] = 1;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int cnt = 0;
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
if(report[j][i] == 1) cnt++;
if(cnt >= k) candidate[i] = 1;
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int cnt = 0;
for(int j=0; j<n; j++) // 회장 후보가 된 학생
if(report[i][j] == 1 && candidate[j] == 1) cnt++;
ans.add(cnt);
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Main T = new Main();
int[][] arr={{0, 1}, {0, 3}, {1, 2}, {2, 0}, {2, 3}, {3, 0}};
System.out.println(T.solution(4, arr, 2));
}
}- python
def solution(board):
answer=0
n=len(board)
row=[0]*n
col=[0]*n
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if board[i][j]>row[i]:
row[i]=board[i][j]
if board[j][i]>col[i]:
col[i]=board[j][i]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
answer+=(min(row[i], col[j])-board[i][j]);
return answer
print(solution([[2, 5, 7, 3], [6, 8, 9, 7], [3, 2, 4, 5], [7, 2, 5, 8]]))
728x90